To change your Firefox language to English (or any other language) you can simply download and reinstall Firefox with your preference language version from this link http://www.mozilla.com/en-US/firefox/all.html after that choose which language you prefer and start downloading. For English language you can use this link http://www.mozilla.com/en-US/products/download.html?product=firefox-3.6&os=win&lang=en-US
Tuesday, November 17, 2009
How to backup bookmarks in Firefox
There is always a chance that Firefox browser may crash due to various reasons such as new theme installation, add-on installation or any other reason. To have a backup data for bookmark in Firefox is always a good idea as you may never know you will need it someday. It only takes seconds to backup your bookmark, and you can choose two methods to do it (to do bookmarks backup for Internet Explorer browser you can click here):
Browser and Browsing Tips and Tricks
Have you seen a browser who surfs in the internet with remarkable speed. Do you know that there's so many interesting ways to make your browsing much faster and easier. Here i discovered some of many cool tips and tricks that might amaze you. Once you memorized and master all of these tricks you would be able to browse like pro:
Note: Some of these shortcuts may only work for Firefox.
Note: Some of these shortcuts may only work for Firefox.
Labels:
Browser and Browsing Tips,
Mozilla Firefox
Firefox Tricks and Tips
Quick search. If you discover a word or phrase during your reading on a website and you want to put it into a search engine? Most probably all of you might open in a new tab, go to Google or any other search engine provider and type the words or phrase in there.
Firefox Tips and Tricks
Address bar. Delete items from address bar history. Your browser has the ability to show previous visited URLs automatically. When you type the name of a website in location bar (address bar), the list of visited URLs will appear. If you do not want it to
How to backup Favorites in Internet Explorer
Follow these simple and easy steps to backup your Favorites in Internet Explorer:
Saturday, November 7, 2009
How to redirect using meta refresh tag
Meta refresh redirect is a way to redirect pages, it sends your visitors from a page to another page using a meta http-equiv tag that you inserted into the header of an html document.
Here’s how to use it:
www.yourdomainname.com/nameofyourfolder and it will automatically redirect the page.
The main disadvantage of this method is that you need a separate file for every redirect.
Note that this method will not cloak your affiliate url in the address box. This basically just do a simple redirection.
By using meta refresh method to redirect, the tag is actually telling the browser to automatically request another page of a site after a certain number of seconds. The content=”” command tells your browser how many second to wait before executing the refresh and the redirection. Becareful of using this method because many SEO experts said that search engines may not like this and they may lower your page rank or even ban you because you are sending visitors to a page other than the one they requested.
Here’s how to use it:
- First, create a folder and name it whatever you like. The name of the folder will be used as part of the url link that you are going to use to redirect. So if your folder’s name is “mysite” then the redirect link will be “www.yoururl.com/mysite”
- Create an html file (you can use a notepad), and place the following script and save it as index.html. Replace “your URL” with the URL which you want to redirect and store the file in the folder which you just created.

- Upload the folder to your hosting account and you are done.
www.yourdomainname.com/nameofyourfolder and it will automatically redirect the page.
The main disadvantage of this method is that you need a separate file for every redirect.
Note that this method will not cloak your affiliate url in the address box. This basically just do a simple redirection.
By using meta refresh method to redirect, the tag is actually telling the browser to automatically request another page of a site after a certain number of seconds. The content=”” command tells your browser how many second to wait before executing the refresh and the redirection. Becareful of using this method because many SEO experts said that search engines may not like this and they may lower your page rank or even ban you because you are sending visitors to a page other than the one they requested.
How to do a PHP redirect
PHP redirect is a way to redirect pages, it sends your visitors from a page to another page using a PHP script. This kind of redirect is said to be more search engine friendly than using Meta Refresh redirect. There’s several reason webmasters need to redirect pages includes making their long url shorter or because the changes they made to their site’s directories. You can easily redirect your readers to a different page using a small snippet of PHP code (or also known as php redirect). Using this method, your visitors can be transfered to the new page witthout having to click a link to continue. Fortunately redirecting pages using PHP is an easy task.
Here’s how to do it:

Here’s how to do it:
- Create and name your new folder. Your folder’s name will be used as part of the url link which you are going to use for redirecting. Let’s say the name of your folder is “mypage” then the redirect link will be www.yoururl.com/mypage
- Create a php file (you can use a notepad), copy paste the following php code below into the notepad and remember to save it as index.php. Replace “your URL” with the URL where you want the redirection to take place and store the file in the folder that you just created.

- Upload the folder to your hosting account and it’s done. Test the new file in all major browsers, like this: www.domainname.com/nameofyourfolder. The redirect should be instantaneous.
How to use PHP include
If you have a website with plenty of pages to update, to edit each page and change it one by one will be very tedious and boring things to do. The more page you have, the more possibility that you make mistakes. Using PHP include is certainly something you need and it is very helpful because not only it enables you to uniform certain parts of your content pages, but also update them all by only editing a single file.
Before you start using PHP includes, make sure that your web host or server can handle PHP files. Secondly, when you are using PHP includes on any pages, make sure the extension of those page is “.php” instead of “.html”. By using this PHP include script, once uploaded to the web, all of your files will merge appropriately to form one page.
Here’s how the PHP code looks like:
The code can be pasted into sidebars, header, tables and anywhere you like.
Change the "filename" to anything you like, to make things easier to remember, it is suggested that you give it a name which correlates to the content you will be putting in it. For example if it is “header.php” then the file should be made especially for header. If the file contains advertisements for your site, then you can name it “ads.php”.
Next, you will want to create a page where the content of this page will appear in the page that contains the PHP include code. Make sure you save it with the exact same name you assigned to the code above, otherwise the script wont work.
Sometimes the path names doesn’t work and therefore you need to use alternative way, that is using the URL in the include instead, like this:
Using this method is less efficient in terms of server resources because (just like a browser) it has to create an HTTP session, get the file and then pull it in (even both of them located at the same server). This method of course is slower than using a pathname.
You can include files with .html, .php, .txt, .asp and other extensions.
Before you start using PHP includes, make sure that your web host or server can handle PHP files. Secondly, when you are using PHP includes on any pages, make sure the extension of those page is “.php” instead of “.html”. By using this PHP include script, once uploaded to the web, all of your files will merge appropriately to form one page.
Here’s how the PHP code looks like:
<?php include("filename.php"); ?>
The code can be pasted into sidebars, header, tables and anywhere you like.
Change the "filename" to anything you like, to make things easier to remember, it is suggested that you give it a name which correlates to the content you will be putting in it. For example if it is “header.php” then the file should be made especially for header. If the file contains advertisements for your site, then you can name it “ads.php”.
Next, you will want to create a page where the content of this page will appear in the page that contains the PHP include code. Make sure you save it with the exact same name you assigned to the code above, otherwise the script wont work.
Sometimes the path names doesn’t work and therefore you need to use alternative way, that is using the URL in the include instead, like this:
<?php include("http://www.domainname.com/directory/filename.php"); ?>
Using this method is less efficient in terms of server resources because (just like a browser) it has to create an HTTP session, get the file and then pull it in (even both of them located at the same server). This method of course is slower than using a pathname.
You can include files with .html, .php, .txt, .asp and other extensions.
Thursday, November 5, 2009
What is Reseller Hosting
Many web hosting firms offer reseller hosting service. With this type of hosting, the account owners of reseller service rent out portion of their disk space and bandwidth they receive to other end users. In this case, the account owners are just like a hosting service provider to those end users.
Labels:
Domain and Hosting
Difference Between Shared Hosting, VPS and Dedicated Hosting
There are basically 3 types of hosting available – shared hosting, VPS hosting and dedicated hosting. Of course there are differences between these three and knowing which type of service is best for your website is very important.
Labels:
Domain and Hosting
Wednesday, November 4, 2009
Set up CO.CC domain on 000webhost account
What is CO.CC? If you've never heard of CO.CC, the following sentence I took directly from the source may explain it to you briefly.
CO.CC will provide us with a domain name free of charge (yourdomainname.co.cc). Since the domain name is free and it’s easy to make, this can be absolutely useful for those who want to make a website and are not ready yet to pay for a domain name. Installing the domain on your web host takes about 5 minutes. I found many people use the CO.CC domain name to replace their Blogspot URL for their custom domain (for example, you will see myblog.co.cc instead of myblog.blogspot.com), you can do it to your Wordpress too or any other blog that support the feature.
If you are interested to get the free domain, start registering, which is easy and fast (each account can only have 2 free domain ending with co.cc). Here are the steps:


Important: Always backup your files after you do an update when you host your site on 000webhost as many users account are closed without any warning or notifications. I had an account in 000webhost and it has suddenly been closed "due to Inactivity" without informing me beforehand. The 000webhost affiliate program is also reported by many people as a scam, you can find this on Google.
“CO.CC is the world's best free domain name registrar and the leading provider of Internet services including - Free dns service, online marketing, url forwarding, e-mail and more.”
CO.CC will provide us with a domain name free of charge (yourdomainname.co.cc). Since the domain name is free and it’s easy to make, this can be absolutely useful for those who want to make a website and are not ready yet to pay for a domain name. Installing the domain on your web host takes about 5 minutes. I found many people use the CO.CC domain name to replace their Blogspot URL for their custom domain (for example, you will see myblog.co.cc instead of myblog.blogspot.com), you can do it to your Wordpress too or any other blog that support the feature.
If you are interested to get the free domain, start registering, which is easy and fast (each account can only have 2 free domain ending with co.cc). Here are the steps:
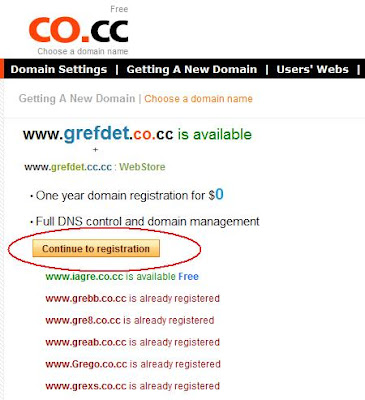
- Click Here to go to CO.CC (will open in a new tab), fill in your domain name of choice in the box provided and press “check”. A page will come up telling you whether that domain name is available. If not, select a new domain name to try. Sometimes it will charge you $3 or $7 for a good domain name you choose, dont be dissapointed, you can ‘slightly’ change your domain name or add extra letter, or number, or insert a hyphen somewhere in it until it’s totally free.
- If your domain name is available, then you can start to press “Continue to registration”.

- A “Create an account” page will come up somewhere around this step (if i’m not wrong) and if it does, fill up all your details needed.
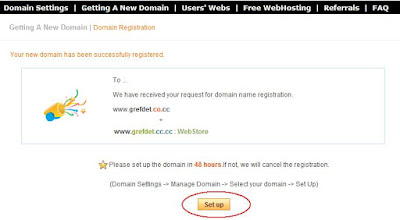
- After that you will reach to a page where it states “Your new domain has been successfully registered”.

- Click “Set up” and you will get 3 option: Name Server, Zone Record, and URL Forwarding.

- Select “Name Server” and you are given a form where you can enterr a couple of name servers. Let's take 000webhost for our tutorial (since it is also free), the 000webhost DNS server addresses are normally ns01.000webhost.com and ns02.000webhost.com (ok, if you want to convince yourself that we will not entering the wrong name server, lets skip this and move on to the next step).
- Open a new tab and go to your 000webhost account (i assume that you’ve already got your free 000webhost account). From the main page, click “Create New” at the top and fill in your new CO.CC domain and your password in the box provided. After you’re done then click “Setup New Account”
 On the new page click "Back to Account List".
On the new page click "Back to Account List".
- After that on the Account List page, you will see the nameservers on top. Those nameservers are the one you have to enter into the Manage DNS box column in the previous step which you had skip.

- Go back to the previous tab where you are on the CO.CC Manage DNS form page. Enter those nameservers and when you finish entering the nameservers, click “Set up” button and the job is done.

Important: Always backup your files after you do an update when you host your site on 000webhost as many users account are closed without any warning or notifications. I had an account in 000webhost and it has suddenly been closed "due to Inactivity" without informing me beforehand. The 000webhost affiliate program is also reported by many people as a scam, you can find this on Google.
Tuesday, November 3, 2009
How to Create Domain Email at Your Hosting Cpanel
Creating our own email address at our own domain is very easy. Most paid website hosting servers have an opstion for creating your email address with your own domain name. This domain email is included with your cost and setting it up is not only free but it can also add a professional touch to your business. This is why many popular websites choose to have their own domain emails under their contact page. You can create a number of different email addresses on your web server but this number varies from one service provider to another.
Labels:
Domain and Hosting,
Email
Sunday, November 1, 2009
Difference between HTML and XHTML
XHTML stands for Extensible HyperText Markup Language. It is a cleaner and stricter version of HTML, also more stable, sharpened and sophisticated version. XHTML, is a combination of XML (Extensible Markup Language) and HTML. XML is designed to describe data, while HTML is designed to display data.
HTML (the original language of World Wide Web) is rapidly being replaced by XHTML. XHTML is similar in most features to HTML due to the fact that XHTML was derived from HTML just to conform with XML standards. There are only a few minor differences between these two markup language, its only that XHTML is designed for being a HTML successor or some call it a better HTML.
HTML (the original language of World Wide Web) is rapidly being replaced by XHTML. XHTML is similar in most features to HTML due to the fact that XHTML was derived from HTML just to conform with XML standards. There are only a few minor differences between these two markup language, its only that XHTML is designed for being a HTML successor or some call it a better HTML.
- One of the XHTML benefit is that it is more accepted in non “computer” devices such as cell phones, palm devices and other scaled down browsers.
- All elements and attributes in XHTML documents have to be written in lower case (while it is not necessarily in HTML).
- All opening tags must be closed with closing tags, in HTML many of these tags were left open and you still can view them in a browser without errors. Items like line breaks or images which are without HTML closing tags should have XHTML self-closing.
- In XHTML, all the tags also have to be properly nested, it means that if you start tag “a” and open another tag within tag “a”, you have to close the latest tag first and then close tag “a” at the last. Although nesting is also followed in HTML but it is not as strict as in XHTML.
- All values for attributes must be encased in double or single quotes and the attributes themselves should not be abbreviated.
- The image tags should be provided with alt attributes which contain the image description in order to allow them have some requirements for accessibility along with different web standard.
- Another XHTML only requirement is the declaration of the DOCTYPE which determines what rules your document will follow, which it inherited from XML. The first line you will see when you switch your XHTML page to the source code is a document type declaration (also called DTD or DOCTYPE) at the top of your XHTML documents. Most web pages being created today will include a doctype declaration. There are 3 DTDs for XHTML: Strict (only will validate if it is without deprecated tags), Transitional (will still validate with deprecated tags), and Frameset (for a page that “sets” up “frames”). All XHTML documents have to conform to the XML syntax rules.
Part 1: HTML Part 2: HTML Attributes Part 3: HTML Table Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
Learn CSS basic codes
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets, is a tool to add layout to your websites. It controls the presentation of web pages. CSS provides information to the browser about how the content on the page should be displayed. CSS covers fonts, lines, margins, width, height, advanced positions and background images. It controls layout of many documents from a single style sheet, apply different layout to different media-types (print, screen, etc) and many more. Compared to HTML, CSS offers more options and is supported by all browsers today.
To structure content html is used, but to format structured content, CSS is used. CSS command consists of three parts: selector – property – value.
Selector comes first, followed by property and then value. Each property and its value is separated by a colon and ended with a semi-colon. They are also have to be surrounded by curly brackets. Example:
Selector: what html element applied in this area
Property: what will be changed to the selector.
Value: the value of what you are going to change.
Note: Don't leave spaces between property value and the units. It only works in IE but not in Opera or Firefox.
CSS can be applied in 3 ways to an html document:
Open the .htm file by double-click it and you will see that the css file will effect the other file in terms of layout or design. You can change the CSS file to update the style of all HTML documents that linking to it.
Some other common CSS coding:
Properties and Values:
Colors and background
color:green; - (choose the color)
background-color:#ff0000; - (choose background color)
background-image:url("mypic.gif"); - (background image)
background-repeat:no-repeat;/repeat;/repeat-x;/repeat-y; - (image background pattern)
Background-attachment:scroll/ fixed - (whether still image or movable)
background-position:2cm 2cm/ 50% 25%/ top right - (image background position)
Font
font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; - (what types of font will be used, a comma appears between alternate values, it means if the browser can’t find Times New Roman, it loads Serif). A comma can also separate multiple selectors.
font-style:italic;/ oblique; - (font style)
font-variant:small-caps;/ normal; - (font variant)
font-weight:bold;/ normal; - (font weight)
font-size:30px;/ 12pt;/ 120%;/1em; - (font size)
Text
text-indent:30px; - (text indent)
text-align:right;/ center;/ justify; - (text align)
text-decoration:underline;/ overline;/ line-through; - (add a line in the text)
letter-spacing:6px; - (space between letters)
text-transform:uppercase;/ lowercase;/ none;
list-style-type:circle;/ square;/ upper-roman; - (list item markers)
p:first-letter{color:#ff0000;font-size:xx-large;} – (to change the first letter of a paragraph)
p:first-line {color:#0000ff;font-variant:small-caps;} –(to change the first line of a paragraph).
Margin, Padding, Border
margin-top/ right/ bottom/ left: 100px; - (position of the margin)
or margin:100px 40px 10px 70px; - (clock-wise= top, right, bottom, left)
padding:20px 20px 20px 80px; - (padding= space between the border and content)
border-width:thick;/ thin;/medium;
border-style:dotted;/ dashed;/ solid;/ double;/ groove;/ ridge;/ inset;/ outset;
border-style:dotted solid double dashed; - (adding different border style from top-right-bottom-left/ clock-wise direction)
border-top/ left/ bottom-color:red; -(apply a color to only one side of a border)
border-bottom/ top/ right-style:solid; -(add style to only one side of a border)
border-top/ left/ bottom-width:thick; -(set the size of a border)
outline:green dotted thick; - (a line drawn around elements (outside the borders).
outline-color:#00ff00;/ style:dotted;/ width:5px;
position:absolute;/ relative; top:150px; left:500px; - (locating an element whether in absolute or relative position)
z-index:1;/2;/3; etc. - (To make an element become layers and the value of its property can be used as an order of which elements overlap one another)
visibility:hidden – (to hide an element, but it still take up the same space as before)
display:none – (to hide an element and it will not take up any space)
max-height:/min-height:/max-width:/min-width:100px; - (set the maximum/ minimum height and width of an element)
display:inline – (to change block element become inline)
display:block – (to change an inline element to a block element)
Selectors:
Link
a:visited - (a visited link)
a:active - (a link the moment it is clicked.)
a:hover - (when you place a cursor over a link)
Class, Id and Div
class="....." - (to specify a style to a particular element or group of elements)
id="....." - (to specify a style for a single, unique element)
span class="....." - (for adding visual features to selected parts of text)
div id="....." - (to group one or more block-level elements)
Comment
/*put your comment here*/ - (you can add comment on top of css coding to explain your code, comments are ignored by browsers)
To structure content html is used, but to format structured content, CSS is used. CSS command consists of three parts: selector – property – value.
Selector {property: value; }
Selector comes first, followed by property and then value. Each property and its value is separated by a colon and ended with a semi-colon. They are also have to be surrounded by curly brackets. Example:
body {background-color: red;}
Selector: what html element applied in this area
Property: what will be changed to the selector.
Value: the value of what you are going to change.
Note: Don't leave spaces between property value and the units. It only works in IE but not in Opera or Firefox.
CSS can be applied in 3 ways to an html document:
- by using the html attribute style (inline) – example:
<body style="background-color: yellow;">
- By inserting the CSS codes between style tag (<style>) – example:
<html>
<head>
<title>Example</title>
<style type="text/css">
body {background-color: yellow;}
</style>
</head>
- By inserting the CSS codes in an external style sheet (a text file with the extension “.css”) and linked to the html document. The link can be created with a line of html code that is inserted in the header section of your html file (between <head> and </head> tag):
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="name-of-the-folder/name-of-the-file.css" />
| Save this to "mypage.htm": | Save this to "style.css": |
| <html> <head> <title>My Page</title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css" /> </head> <body> <h1>Hello, I’m Edy Bright</h1> </body> </html> | body {
background-color: red; } |
Open the .htm file by double-click it and you will see that the css file will effect the other file in terms of layout or design. You can change the CSS file to update the style of all HTML documents that linking to it.
Some other common CSS coding:
Properties and Values:
Colors and background
color:green; - (choose the color)
background-color:#ff0000; - (choose background color)
background-image:url("mypic.gif"); - (background image)
background-repeat:no-repeat;/repeat;/repeat-x;/repeat-y; - (image background pattern)
Background-attachment:scroll/ fixed - (whether still image or movable)
background-position:2cm 2cm/ 50% 25%/ top right - (image background position)
Font
font-family:"Times New Roman", serif; - (what types of font will be used, a comma appears between alternate values, it means if the browser can’t find Times New Roman, it loads Serif). A comma can also separate multiple selectors.
font-style:italic;/ oblique; - (font style)
font-variant:small-caps;/ normal; - (font variant)
font-weight:bold;/ normal; - (font weight)
font-size:30px;/ 12pt;/ 120%;/1em; - (font size)
Text
text-indent:30px; - (text indent)
text-align:right;/ center;/ justify; - (text align)
text-decoration:underline;/ overline;/ line-through; - (add a line in the text)
letter-spacing:6px; - (space between letters)
text-transform:uppercase;/ lowercase;/ none;
list-style-type:circle;/ square;/ upper-roman; - (list item markers)
p:first-letter{color:#ff0000;font-size:xx-large;} – (to change the first letter of a paragraph)
p:first-line {color:#0000ff;font-variant:small-caps;} –(to change the first line of a paragraph).
Margin, Padding, Border
margin-top/ right/ bottom/ left: 100px; - (position of the margin)
or margin:100px 40px 10px 70px; - (clock-wise= top, right, bottom, left)
padding:20px 20px 20px 80px; - (padding= space between the border and content)
border-width:thick;/ thin;/medium;
border-style:dotted;/ dashed;/ solid;/ double;/ groove;/ ridge;/ inset;/ outset;
border-style:dotted solid double dashed; - (adding different border style from top-right-bottom-left/ clock-wise direction)
border-top/ left/ bottom-color:red; -(apply a color to only one side of a border)
border-bottom/ top/ right-style:solid; -(add style to only one side of a border)
border-top/ left/ bottom-width:thick; -(set the size of a border)
outline:green dotted thick; - (a line drawn around elements (outside the borders).
outline-color:#00ff00;/ style:dotted;/ width:5px;
position:absolute;/ relative; top:150px; left:500px; - (locating an element whether in absolute or relative position)
z-index:1;/2;/3; etc. - (To make an element become layers and the value of its property can be used as an order of which elements overlap one another)
visibility:hidden – (to hide an element, but it still take up the same space as before)
display:none – (to hide an element and it will not take up any space)
max-height:/min-height:/max-width:/min-width:100px; - (set the maximum/ minimum height and width of an element)
display:inline – (to change block element become inline)
display:block – (to change an inline element to a block element)
Selectors:
Link
a:visited - (a visited link)
a:active - (a link the moment it is clicked.)
a:hover - (when you place a cursor over a link)
Class, Id and Div
class="....." - (to specify a style to a particular element or group of elements)
id="....." - (to specify a style for a single, unique element)
span class="....." - (for adding visual features to selected parts of text)
div id="....." - (to group one or more block-level elements)
Comment
/*put your comment here*/ - (you can add comment on top of css coding to explain your code, comments are ignored by browsers)
Part 1: HTML Part 2: HTML Attributes Part 3: HTML Table Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
What's the difference between HTML and XHTML What is CSS?
What's the difference between HTML and XHTML What is CSS?
Colspan and Rowspan in HTML Table
Part 1: HTML
Part 2: HTML Attributes
Part 3: HTML Table
Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
Colspan and rowspan are html attributes used to span table cells across more than a column or row. Colspan is short for “column span” or indicates “how many across” while a rowspan indicates “how many down”.
Colspan is used within a <td> tag to specify how many columns it should span.
Here, i give you the example:
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td colspan="5">Cell 1-5 combined</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 1</td>
<td>Cell 2</td>
<td>Cell 3</td>
<td>Cell 4</td>
<td>Cell 5</td>
</tr>
</table>
and here is the outcome:
By setting colspan to "5", the cell in the first row spans five columns. Here below is another example for better understanding:
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td colspan="3">Cell 1-3</td>
<td>Cell A</td>
<td>Cell B</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 1</td>
<td>Cell 2</td>
<td>Cell 3</td>
<td>Cell 4</td>
<td>Cell 5</td>
</tr>
</table>
Here when you see in a browser:
Rowspan sets how many rows a cell spans.
Example:
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td rowspan="5">Cell 1-5</td>
<td>Cell 1</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 3</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 5</td>
</tr>
</table>
and here the result when you see in the browser:
Not as hard as you think right?, and with a number of practices, it should get easier and you might get used to it :)
Part 2: HTML Attributes
Part 3: HTML Table
Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
Colspan and rowspan are html attributes used to span table cells across more than a column or row. Colspan is short for “column span” or indicates “how many across” while a rowspan indicates “how many down”.
Colspan is used within a <td> tag to specify how many columns it should span.
Here, i give you the example:
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td colspan="5">Cell 1-5 combined</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 1</td>
<td>Cell 2</td>
<td>Cell 3</td>
<td>Cell 4</td>
<td>Cell 5</td>
</tr>
</table>
and here is the outcome:
Cell 1-5 combined
| ||||
| Cell 1 | Cell 2 | Cell 3 | Cell 4 | Cell 5 |
By setting colspan to "5", the cell in the first row spans five columns. Here below is another example for better understanding:
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td colspan="3">Cell 1-3</td>
<td>Cell A</td>
<td>Cell B</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 1</td>
<td>Cell 2</td>
<td>Cell 3</td>
<td>Cell 4</td>
<td>Cell 5</td>
</tr>
</table>
Here when you see in a browser:
Cell 1-3
| Cell A | Cell B | ||
| Cell 1 | Cell 2 | Cell 3 | Cell 4 | Cell 5 |
Rowspan sets how many rows a cell spans.
Example:
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td rowspan="5">Cell 1-5</td>
<td>Cell 1</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 3</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 5</td>
</tr>
</table>
and here the result when you see in the browser:
| Cell 1-5 | Cell 1 |
| Cell 2 | |
| Cell 3 | |
| Cell 4 | |
| Cell 5 |
Not as hard as you think right?, and with a number of practices, it should get easier and you might get used to it :)
Using HTML codes to create Tables
Part 1: HTML
Part 2: HTML Attributes
Part 3: HTML Table
Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
Tables are defined with <table> tag and it is made of rows (<tr>) and columns (<td>). Tr means table row and td means table data.
Part 2: HTML Attributes
Part 3: HTML Table
Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
Tables are defined with <table> tag and it is made of rows (<tr>) and columns (<td>). Tr means table row and td means table data.
- To start creating table, you need an opening table tag, which is <table> and to end it, is to use table closing tag which is </table>.
- To start creating horizontal table rows you need the opening tag <tr> and after entering number of column/s you need to end it with a closing tag </tr>.
- To start making column in the table, as usual you need the opening tag <td> and after entering all the data, close it with a closing tag which is <td>.
What is attributes in HTML
Part 1: HTML
Part 2: HTML Attributes
Part 3: HTML Table
Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
What is an attributes in HTML?
Attribute is an additional command towards the element which are written after a start tag and come in name/value pairs like: name=”value”. The values are always enclosed in quotes.
Here are the examples of attribute:
Part 2: HTML Attributes
Part 3: HTML Table
Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
What is an attributes in HTML?
Attribute is an additional command towards the element which are written after a start tag and come in name/value pairs like: name=”value”. The values are always enclosed in quotes.
Here are the examples of attribute:
What is HTML and how to use it
Part 1: HTML
Part 2: HTML Attributes
Part 3: HTML Table
Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, it is a language (computer language) to tell your browser how a page should be displayed, which makes it possible to present information, showing pictures, graphics and etc. The language consists of codes, and there are plenty different codes for all sorts of formatting. When you view a page from a browser, what you see is the browser’s interpretation of HTML.
You can see the HTML codes of a page on the internet by simply clicking “View” and then select “Source” or if you are using Firefox browser you can press Ctrl + U on your keyboard to view the codes. For people who do not know what is or how to use the codes, HTML code can be very complicated and scary to them. The good news is that HTML is very easy to learn and understand, if you want to build your own website you need to learn what is HTML and how to use it.
The HTML codes consists of tags (markup tags or usually called as HTML tags), and the tag itself consists of keyword inside angle brackets. Most HTML tags start with an opening tag and end with a closing tag. A HTML document has 2 parts: a head (information about the page, anything you put here will not be displayed on the page) and a body (information that constitutes the page, anything you put here will be displayed on the page).
Still get confused? Well, i think it’s better if we put it into practice. Practice can explain and make you understand much better rather than just theory.
Open a Notepad, copy and paste he following HTML codes:
<html>
<head>
<title>This is my first website</title>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>This is the first sentence</b></p>
<p><i>This is the second sentence</i></p>
<p><U>This is the third sentence</u></p>
</body>
</html>
Save your notepad and name it “mypage.htm”, don’t forget to choose “All Files” otherwise you save it as a text document and not HTML document.
 The ending “.htm” means that it is an HTML document, you also can name it with the ending of “.html”, it gives the same result. After that go and open the document by double-clicking the file. See and notice what happen to each of the sentence, different tag you apply to each of the line produce different effect to the text.
The ending “.htm” means that it is an HTML document, you also can name it with the ending of “.html”, it gives the same result. After that go and open the document by double-clicking the file. See and notice what happen to each of the sentence, different tag you apply to each of the line produce different effect to the text.
Here another common basic HTML commands:
<b> means "bold"
<i> means "italics"
<em> means "emphasis"
<u> means "underline"
<h1> means "heading 1"
<br> means "break"
<p> means "paragraph"
<hr> means "horizontal"
<ul> means "unordered list"
<ol> means "ordered list"
It doesn’t matter whether you type the tags in uppercase or lowercase, it will give the same result.
In the HTML code, there is attribute. Attribute also plays one of the most important role, but what is it? Let us discuss it in the next page.
Part 2: HTML Attributes
Part 3: HTML Table
Part 4: Colspan and Rowspan
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, it is a language (computer language) to tell your browser how a page should be displayed, which makes it possible to present information, showing pictures, graphics and etc. The language consists of codes, and there are plenty different codes for all sorts of formatting. When you view a page from a browser, what you see is the browser’s interpretation of HTML.
You can see the HTML codes of a page on the internet by simply clicking “View” and then select “Source” or if you are using Firefox browser you can press Ctrl + U on your keyboard to view the codes. For people who do not know what is or how to use the codes, HTML code can be very complicated and scary to them. The good news is that HTML is very easy to learn and understand, if you want to build your own website you need to learn what is HTML and how to use it.
The HTML codes consists of tags (markup tags or usually called as HTML tags), and the tag itself consists of keyword inside angle brackets. Most HTML tags start with an opening tag and end with a closing tag. A HTML document has 2 parts: a head (information about the page, anything you put here will not be displayed on the page) and a body (information that constitutes the page, anything you put here will be displayed on the page).
Still get confused? Well, i think it’s better if we put it into practice. Practice can explain and make you understand much better rather than just theory.
Open a Notepad, copy and paste he following HTML codes:
<html>
<head>
<title>This is my first website</title>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>This is the first sentence</b></p>
<p><i>This is the second sentence</i></p>
<p><U>This is the third sentence</u></p>
</body>
</html>
Save your notepad and name it “mypage.htm”, don’t forget to choose “All Files” otherwise you save it as a text document and not HTML document.
 The ending “.htm” means that it is an HTML document, you also can name it with the ending of “.html”, it gives the same result. After that go and open the document by double-clicking the file. See and notice what happen to each of the sentence, different tag you apply to each of the line produce different effect to the text.
The ending “.htm” means that it is an HTML document, you also can name it with the ending of “.html”, it gives the same result. After that go and open the document by double-clicking the file. See and notice what happen to each of the sentence, different tag you apply to each of the line produce different effect to the text.Here another common basic HTML commands:
| <HTML> </HTML> | To create a Web page. All Web pages must have this command. |
| <HEAD> </HEAD> | All the head elements are written here, anything you put inside a head tag will not be displayed on the page. Elements inside head tag include scripts, meta information, instruct the browser where to find style sheets and more. |
| <TITLE> </TITLE> | Displays the Title in the title bar area. |
| <BODY> </BODY> | Anything you put inside the body tag will be displayed on the page and will be shown in the browsers to users. |
| <B> </B> or <strong> </strong> | The text will be shown in Bold |
<I> </I> or <em> </em> | The text will be shown in Italics |
| <u> </u> | To underline a text or words. |
| <strike> </strike> | |
| <CENTER> </CENTER> | |
| <H1> </H1> | Heading 1 |
| <H2> </H2> | Heading 2 |
| <H3> </H3> | Heading 3 |
| <H4> </H4> | Heading 4 |
| <H5> </H5> | Heading 5 |
| <H6> </H6> | Heading 6 |
| <BR> | New Line. Creates single space bettween lines. |
| <P> </p> | New paragraph. Creates double space between lines, paragraphs. |
| | To add a space. |
| <HR> | Produces a horizontal rule across document. |
| <ul> <li>A list</li> <li>Another list</li> </ul> |
|
| <ol> <li>First list</li> <li>Second list</li> </ol> |
|
<b> means "bold"
<i> means "italics"
<em> means "emphasis"
<u> means "underline"
<h1> means "heading 1"
<br> means "break"
<p> means "paragraph"
<hr> means "horizontal"
<ul> means "unordered list"
<ol> means "ordered list"
It doesn’t matter whether you type the tags in uppercase or lowercase, it will give the same result.
In the HTML code, there is attribute. Attribute also plays one of the most important role, but what is it? Let us discuss it in the next page.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
